Build a Telegram bot with Ghost

Overview
This tutorial demonstrates how to create a Telegram bot that monitors and announces new deposits on the blockchain using Ghost. The bot sends beautifully formatted messages with transaction details and celebratory GIFs to your specified Telegram channels.
For the purposes of this example, we'll monitor deposits on Zeru Finance.
What is Ghost and Why Does It Matter?
Ghost is a next-gen indexing stack that empowers developers to build GraphQL APIs for extracting, transforming, storing, and querying blockchain data.
What sets Ghost apart from other indexers:
-
Write indexers in the same language as your smart contracts (Solidity) - Since smart contract developers emit critical events for indexers, they should be able to write the indexers themselves without needing to learn new languages or tools.
-
Fully browser-based - Ghost requires no command-line tools or downloads. Everything is built and deployed directly from your browser, streamlining the developer experience.
-
Blazing-fast performance - Deploy indexers (subgraphs) in seconds, drastically reducing setup time and increasing efficiency for real-time blockchain data access.
Ghost is designed to make blockchain data indexing more intuitive, seamless, and efficient for smart contract developers.
Prerequisites
To follow along, you'll need:
- A Ghost account to create our indexer for tracking events emitted by Zeru Finance's smart contract
Getting Started
Navigate to the Ghost Graph dashboard and click the Create Graph button. This will
open a modal where you can name your graph. Enter "Zeru Telegram" and select Bartio from the dropdown.
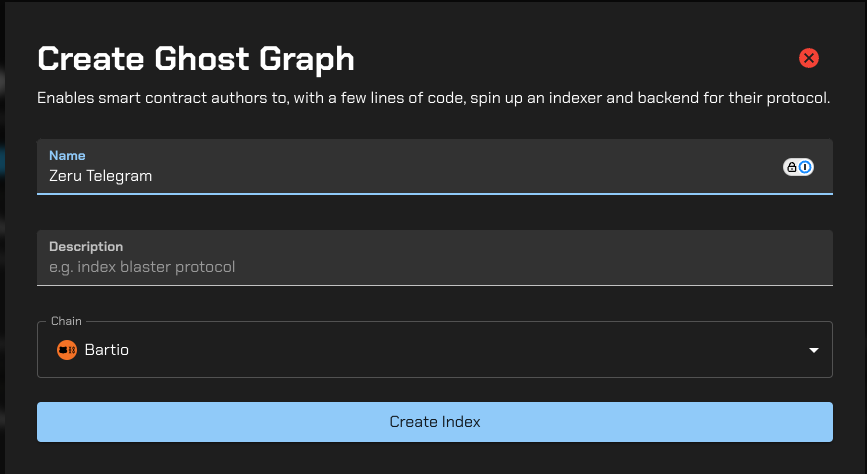
Click on the newly created graph to access the code editor.
Code Editor
There are three essential files in the code editor that you need to understand:
- Events.sol
- Schema.sol
- Indexer.sol
Events.sol
Smart contracts emit events for users to track. In this file, we define the specific events we want to monitor. For this
example, we'll track the Deposit event from Zeru's smart contract. Copy and paste this code into your events.sol
file:
interface Events {
event Deposit(address indexed reserve, address user, address indexed onBehalfOf, uint256 amount, uint16 indexed referral);
}
Schema.sol
The schema file allows us to define entities as Solidity structs. You can think of an entity as an object with multiple properties. These entities will be created and updated (covered in the next section) and can be queried after deployment.
For our purpose, we'll create a Deposit entity. Copy and paste this code:
struct Deposit {
string id;
address reserve;
address userId;
address onBehalfOf;
uint256 amount;
uint16 referral;
uint32 timestamp;
uint64 block;
bytes32 txHash;
}
Click the generate button to create the necessary files, including the indexer.sol file that you'll need to modify.
Indexer.sol
After reviewing the events and schema, we'll work with indexer.sol, which contains the core indexing logic. Here, we
register the contract addresses we want to monitor for events.
Register Zeru's smart contract using the graph.registerHandle function:
address constant ZERU_LENDING_POOL = 0x61dF6c455f1119d174F46B41a4BF39ac9Dedb4e4;
function registerHandles() external {
graph.registerHandle(ZERU_LENDING_POOL);
}
We also define transformation functions for each event type (as defined in events.sol). These functions allow us to
retrieve an entity, update it using event data, and save the updated entity.
For example, when a Deposit event is emitted, we perform a transformation by creating a new Deposit object,
populating it with event parameters, and storing it in the respective fields within a struct. Finally, we save the
entity using graph.saveDeposit(deposit), making it available for future queries.
Add this code to your indexer.sol file:
function onDeposit(EventDetails memory details, DepositEvent memory ev) external {
Deposit memory deposit = graph.getDeposit(details.uniqueId());
deposit.reserve = ev.reserve;
deposit.userId = ev.user;
deposit.onBehalfOf = ev.onBehalfOf;
deposit.amount = ev.amount;
deposit.referral = ev.referral;
deposit.timestamp = details.timestamp;
deposit.block = details.block;
deposit.txHash = details.transactionHash;
graph.saveDeposit(deposit);
}
Compile and Deploy
After reviewing all files, compile and deploy your Ghost Graph. Within seconds, your Ghost Graph should be fully deployed and synchronized with the chain. You'll see the number of entities stored in your graph and have access to various exploration options.
Click the playground button to launch your GraphQL playground.
GraphQL Playground
Copy this query into your playground and click the play button to query your graph:
query GetLatestDeposits {
deposits(orderBy: "timestamp", orderDirection: "desc") {
items {
amount
block
id
onBehalfOf
referral
reserve
timestamp
txHash
userId
}
}
}
This will display all the latest deposits.
Create and Configure Telegram Bot
After setting up the Ghost Graph, let's configure the Telegram bot to announce new deposits.
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/tryghostxyz/ghost-tg-bot
cd ghost-tg-bot
- Create your environment configuration by copying the example file:
cp .env.example .env
Setting Up Environment Variables
You'll need to configure three essential environment variables in your .env file:
-
TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN
- Create a new bot through @BotFather on Telegram
- Send
/newbotto BotFather and follow the prompts - Copy the provided token to
TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKENin your.envfile
-
GHOST_GRAPH_URL
- Go to your deployed Ghost Graph
- Click the "Deploy" button
- Copy the provided query URL to
GHOST_GRAPH_URL
-
CHANNEL_IDS
- Add your bot as an admin to your target Telegram channels
- To get a channel's ID:
- Open your channel in web.telegram.org
- Find the channel ID in the URL after the hash (#)
- Replace
#-with-100 - Example:
#-1234564363becomes-1001234564363
- For multiple channels, separate IDs with commas
Your .env file should look like this:
TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN=1234567890:ABCdefGHIjklMNOpqrsTUVwxyz
GHOST_GRAPH_URL=https://api.ghostlogs.xyz/gg/pub/uniqueIdHere/ghostgraph
CHANNEL_IDS=<YOUR_CHANNEL_ID>
Starting the Bot
- Install the required dependencies:
npm install
# or
yarn install
- Start the bot:
npm start
# or
yarn start
Verification and Troubleshooting
Once running, the bot will monitor for new deposits and send notifications to your specified channels. Each notification includes:
- Deposit amount in ETH
- User address (with explorer link)
- Reserve address (with explorer link)
- Transaction hash (with explorer link)
- Timestamp
- A celebratory GIF
If you encounter issues:
-
Bot not sending messages?
- Verify the bot has admin privileges in the channel
- Double-check your channel IDs
- Confirm your
TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKENis correct
-
No events being received?
- Verify your Ghost Graph is properly deployed
- Check that the
GHOST_GRAPH_URLis correct - Ensure the query URL endpoint is accessible
For additional support, join the Ghost Telegram community.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You've successfully created a system that tracks smart contract events using Ghost, queries the responses, and uses a Telegram bot to send new deposit notifications to your Telegram channel.
What other events will you track?
Join Ghost Community
Twitter: @0xGhostLogs
Telegram: Ghost Devs TG Community
